Ultrasonic Welding for Wiring Harness
-
 @
Mark Ji
@
Mark Ji
- Last updated
Table of Contents
Preface
Wiring harness is a system of wires, connectors, terminals, and other components that transmit electrical signals and power throughout a vehicle or a device. Wiring harness is essential for the safety and performance of various applications, such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial. However, wiring harness is also exposed to various environmental conditions, such as heat, cold, dust, dirt, moisture, and chemicals, which can affect its performance and reliability. Therefore, it is important to protect and maintain the wiring harness from these factors, especially the electrical connections and components.
Introduction
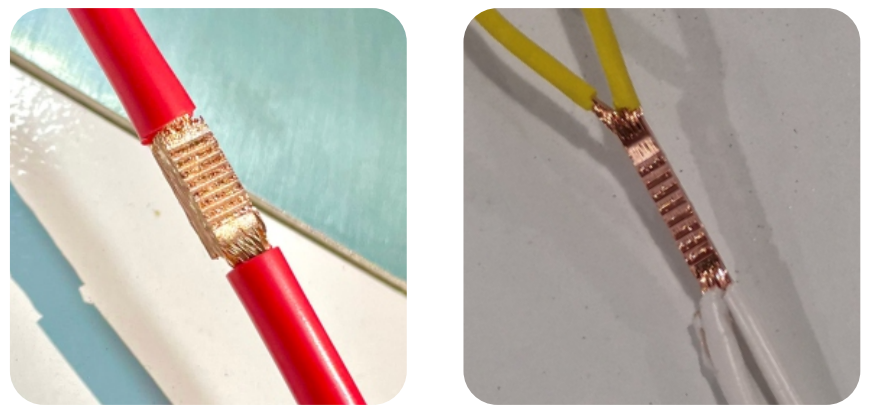
One of the most common and effective methods of protecting and maintaining the electrical connections and components in the wiring harness is ultrasonic welding. Ultrasonic welding is a joining technique that uses high-frequency vibrations to generate heat and melt materials at the joint interface, fusing them together. Ultrasonic welding can be used to join different types of materials, such as metals, plastics, and composites, without using any external heat, filler, or solvent. Ultrasonic welding can also be used to join different shapes and sizes of materials, such as wires, cables, terminals, contacts, and connectors.
Ultrasonic welding offers several benefits over other methods
• Speed: Ultrasonic welding can complete a joint in a fraction of a second, making it one of the fastest joining techniques available. Ultrasonic welding can also reduce the cycle time and increase the productivity of the wiring harness manufacturing process.
• Quality: Ultrasonic welding can produce strong and durable joints that can withstand mechanical and electrical stresses, such as tension, vibration, and current. Ultrasonic welding can also produce consistent and reliable joints that can meet the quality standards and specifications of the wiring harness industry.
• Efficiency: Ultrasonic welding can consume less energy and material than other joining techniques, making it one of the most efficient and economical joining techniques available. Ultrasonic welding can also reduce the waste and emissions generated by the wiring harness manufacturing process, making it more environmentally friendly.
• Flexibility: Ultrasonic welding can be adapted to different types and sizes of materials, as well as different types and formats of joints, making it one of the most versatile and flexible joining techniques available. Ultrasonic welding can also be integrated with other processes and technologies, such as automation, robotics, and vision systems, making it more convenient and user-friendly.
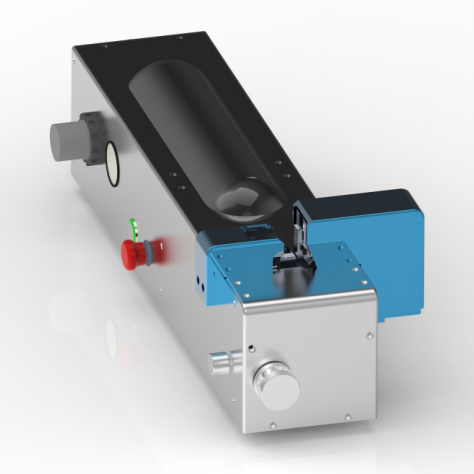

Operation Videos of HH-X0
HH-X0 https://youtube.com/shorts/orj6KLl_gGs
HH-X0 https://youtube.com/shorts/2Jwl1Cd1jdg 7*UL1005 AWG16 wires
Principles and Functions of Ultrasonic Welding
Ultrasonic welding works by converting electrical energy into mechanical energy, which is then transmitted to the materials to be joined through a tool called a sonotrode or a horn. The sonotrode vibrates at a high frequency, typically between 20 and 70 kHz, and applies pressure to the materials, creating friction and heat at the joint interface. The heat melts the materials, forming a molten layer that bonds them together. The sonotrode then stops vibrating and applies a holding pressure to the joint, allowing the materials to cool and solidify, forming a solid joint.
The quality and performance of the ultrasonic welding process depend on several factors, such as the frequency, amplitude, pressure, and time of the sonotrode vibration, as well as the type, shape, and condition of the materials to be joined. These factors can be adjusted and controlled by a device called a generator or a power supply, which converts the electrical energy into the mechanical energy for the sonotrode. The generator can also monitor and record the parameters and data of the ultrasonic welding process, such as the power, energy, displacement, and force of the sonotrode, as well as the temperature, resistance, and impedance of the joint. These parameters and data can be used to evaluate and optimize the ultrasonic welding process, as well as to ensure the quality and consistency of the joints.
Operation Videos of HH-X0
https://youtube.com/shorts/zAxLBp05e0g https://youtube.com/shorts/4u2luPG0sxY
Types of Joints of Ultrasonic welding
• Wire to wire: Ultrasonic welding can be used to join two or more wires together, forming a splice or a junction. Ultrasonic welding can join wires of different or same materials, such as copper, aluminum, or steel, as well as different or same cross-sections, such as round, flat, or stranded. Ultrasonic welding can also join wires in different configurations, such as parallel, perpendicular, or angular.
• Wire to terminal: Ultrasonic welding can be used to join a wire to a terminal, forming a connection or a contact. Ultrasonic welding can join wires to terminals of different or same materials, such as copper, brass, or steel, as well as different or same shapes, such as ring, fork, or blade. Ultrasonic welding can also join wires to terminals in different orientations, such as inline, offset, or side.
• Wire to component: Ultrasonic welding can be used to join a wire to a component, forming a circuit or a device. Ultrasonic welding can join wires to components of different or same materials, such as copper, plastic, or ceramic, as well as different or same functions, such as resistor, capacitor, or sensor. Ultrasonic welding can also join wires to components in different locations, such as surface, through-hole, or edge.
Conclusion
Ultrasonic welding is a simple but effective method of joining materials in the wiring harness, which is vital for the safety and performance of various applications, such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial. Ultrasonic welding can prevent electrical and mechanical problems, such as corrosion, short circuits, and fires, that can affect the wiring harness and the devices it connects. Ultrasonic welding can also improve the appearance and performance of the wiring harness, by reducing noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH), and by ensuring a stable and consistent electrical flow. Ultrasonic welding can be done in different ways, depending on the type and size of the materials, and the type and format of the joints.