FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) Processing
-
 @
Mark Ji
@
Mark Ji
- Last updated
Table of Contents
What is FPC?
FPC, or Flexible Printed Circuit, is a type of circuit board that is made of a thin and flexible polymer film, such as polyimide or polyester, on which conductive traces are printed. FPC can be bent, folded, or twisted to fit into various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for applications that require high-density, miniaturized, and complex wiring. FPC can also provide advantages such as lightweight, low cost, high reliability, and good heat dissipation.
FPC can be classified into different types, such as single-sided, double-sided, multilayer, rigid-flex, and flex-rigid. Single-sided FPC has only one layer of conductive traces on one side of the film. Double-sided FPC has two layers of conductive traces on both sides of the film, which are connected by plated-through holes. Multilayer FPC has more than two layers of conductive traces, which are stacked and bonded together by adhesive or thermal compression. Rigid-flex FPC combines rigid and flexible substrates, which are connected by conductive traces or connectors. Flex-rigid FPC is similar to rigid-flex FPC, but the rigid part can also be bent or folded.
FPC can be used for various purposes, such as electrical insulation, mechanical protection, environmental sealing, identification, and organization. FPC can also be integrated with other components, such as resistors, capacitors, sensors, LEDs, and ICs, to form functional and operational circuits or devices.
How to crimp FPC?
Crimping FPC is the process of attaching FPC to a connector or a terminal, using a tool called a crimper, that applies pressure and force to the FPC and the connector or the terminal, creating a secure and reliable electrical and mechanical connection. Crimping FPC can be done manually or automatically, depending on the size and quantity of the FPCs.
Manual crimping FPC involves using a hand-held crimper to crimp the FPC to the connector or the terminal by hand. Manual crimping FPC can be more flexible and customizable, but also more time-consuming and labor-intensive.
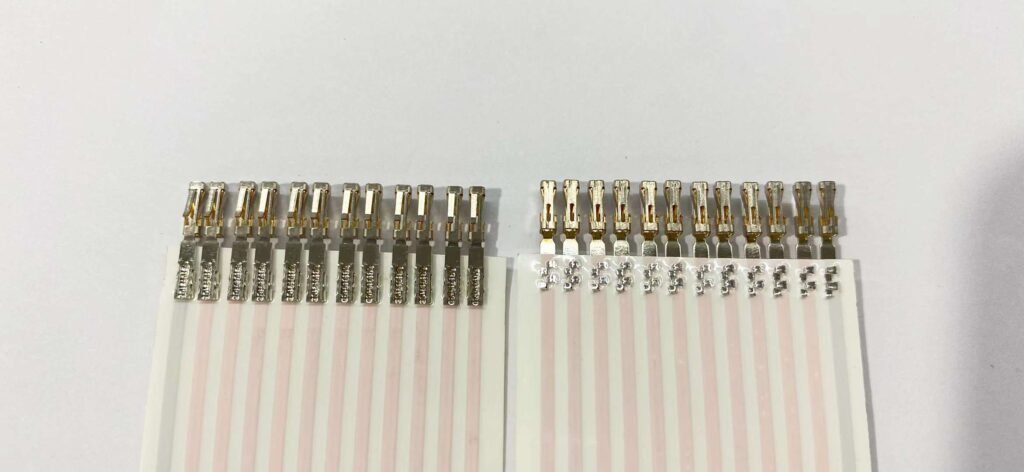

HH-554B https://youtube.com/shorts/tBSFiNGmI1c
Automatic crimping FPC involves using a machine, such as a crimping press, a crimping station, or a crimping system, to crimp the FPC to the connector or the terminal in a controlled and consistent manner. Automatic crimping FPC can be more fast and efficient, but also more rigid and standardized.
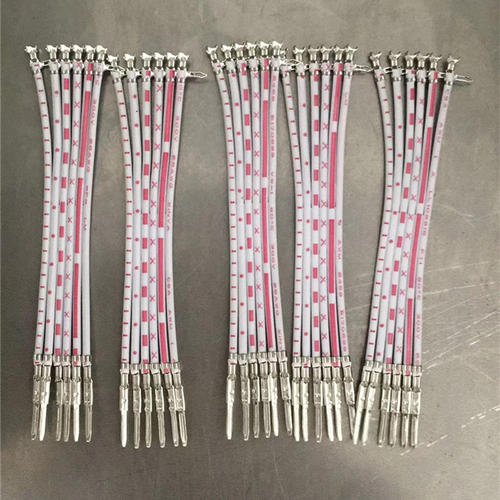

Advantages of FPC
• Flexibility: FPC can be bent, folded, or twisted to fit into various shapes and sizes, making it suitable for applications that require high-density, miniaturized, and complex wiring. FPC can also accommodate bends, curves, and branches in the wiring, without compromising the protection or insulation.
• Weight: FPC is lightweight and does not add much bulk to the wiring, reducing the fuel consumption and emissions of the vehicle, as well as improving the handling and performance.
• Ease of installation: FPC is easy to apply and remove, without requiring special tools or equipment. FPC can also be cut and spliced as needed, without affecting the integrity or functionality of the wiring.
• Versatility: FPC can provide different levels of protection and insulation, depending on the type and quality of the film and the shield. FPC can also be used for various purposes, such as electrical insulation, mechanical protection, environmental sealing, identification, and organization. FPC can also be integrated with other components, such as resistors, capacitors, sensors, LEDs, and ICs, to form functional and operational circuits or devices.
Summary
FPC is a simple but effective way of wiring and connecting various devices and systems, which is vital for the safety and performance of various applications, such as automotive, aerospace, medical, and industrial. FPC can prevent electrical and mechanical problems, such as noise, distortion, or loss of signal, that can affect the quality and functionality of the devices and systems. FPC can also improve the appearance and performance of the devices and systems, by reducing the size and weight, increasing the strength and durability, and ensuring the compatibility and compliance of the devices and systems.