Application of Terminal in Automobile Wire Harness(A)
-
 @
Mark Ji
@
Mark Ji
- Last updated
Table of Contents
Functional Parts of A Terminal

1)The self-locking port of the terminal generally has three positions, the front port, the back port and the two sides of the terminal, its function is to fix the terminal in the receptacle and prevent the terminal from dropping out of the receptacle.
2)The conductor crimp zone between the conductor and the terminal through which the current and signal are transmitted between the terminal and the wire and electrical appliances.
At the same time, it is also the most important zone to ensure electrical and mechanical properties.
3)The insulation crimp zone between the wire insulation and the terminal wings, has two functions:
① to prevent the wire core exposed at the end of the receptacle caused by the retraction of the wire insulation, and the phenomenon of arc connection short circuit occurs under the condition of high voltage.
② after the terminal tail and the wire are wrapped in contact in the insulation crimp zone, the swing amplitude between the wire and the terminal is limited to prevent the possibility of the wire core being broken due to the large swing.

4)Fixed guide rail is a guiding part for a terminal be inserted into the receptacle, and it has 2 main functions:
① play a guiding role when the terminal is loaded into the receptacle.
② it plays the role of fixing the terminal, so that the terminal can not rotate or swing left and right in the receptacle, so as to ensure the assemblability and stability between the terminal and the terminal, the terminal and the receptacle.
5)Belt cut point is the position where the crimping applicator separates the terminal from the belt in the process of cold crimping.
6)In order to protect the wire conductor from being damaged in the conductor crimp zone in the process of crimping, the front and rear bell mouths are left after extrusion deformation during crimping.
7)Crimp pretrudance is the wire conductor in front of the front bell mouth after crimping.
8)The buffer transition zone is the area between the conductor crimping zone and the insulation crimping zone in the process of crimping, which mainly acts as the area of deformation and stress diffusion caused by cold crimping.
Functional Zones of A Terminal
Figure 2 shows three kinds of terminals with different self-locking positions.
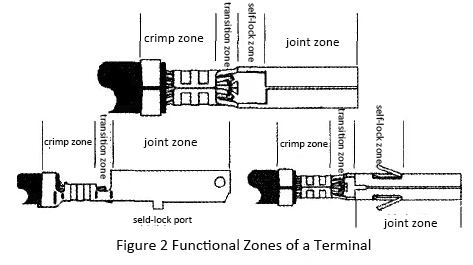
1)Crimping zone is the area where the terminal is in full contact with the conductor. It is the extrusion deformation area of the applicator crimping on the terminal, including conductor crimping area and the insulation crimping area.
2)Transition zone is where between crimping zone and joint zone,or crimping zone and self-locking zone.
3)Self-locking area is where the terminal is self-locked, that is, the area where the terminal and the receptacle is fixed and locked. 4)Joint zone is the area of full contact between the male and female terminals when they are installed together for the transmission of current or signals.

Important Control Parameters of Terminal Crimping
1.Length of Crimp Pretrudance
The length of the terminal crimp pretrudance has a serious influence on the performance of the crimped terminal, and two requirements must be met in practical application.

①Only when the crimp pretrudance is visible, can more effectively ensure the tension of the crimped terminal meet the mechanical properties;
②The crimp pretrudance can not be extended to the joint zone and self-locking zone of the terminal, otherwise it will affect the assembly performance of the terminal and the receptacle, so that the terminal can not be normally installed in the receptacle. And at the same time, it will also affect the ideal contact between the male and female terminals. Sometimes it also leads to incomplete assembly and locking between jackets. The numerical value of the crimping pretrudance length is determined by the characteristics of the terminal itself. Different specifications of terminals have different requirements for it, and the terminals designed by different manufacturers have different requirements.

2. Visible Length of Conductor and Insulaton after Crimping
The position of the conductor and insulation in the buffer transition zone is one of the very important factors in the quality of the terminal crimping process, and the conductor and insulation must be visible in this area.
The best crimping requires that the exposed length of the conductor and insulation in the buffer transition zone is equal, but it is difficult to achieve this in practical application, but both must be visible at the same time.
When the conductor is not visible in this area, it means that the wire insulation layer is pressed into the conductor crimping zone, resulting in a decrease in electrical performance after crimping; when the insulation layer in this area is not visible, it means that the wire insulation layer is not pressed correctly by the terminal, the wire conductor is not protected, and the wire conductor may be broken during use, resulting in a decline in electrical performance and serious safety accidents.
The following examples are used to analyze the requirements of different manufacturers and users for conventional terminal parameters.
Some Japanese enterprises stipulate the position parameters of conductor and insulation in the transition zone as follows: the length between the front wire stripping port and the insulation crimping zone is 0~1mm.
MOLEX, DELPHI, YAZAKI, AMP, KET, JST require that the wire insulation and wire core between the insulation layer and the conductor crimping zone must be visible.
(to be continued)